Siemens Solar Panels direct from Bullnet
![]()
|
A lot of hope is placed on the development of low cost solar cells to ease our energy problems, and yet the entire terrestrial photovoltaic industry is only about 25 years old. The first practical solar cells were made less than 30 years ago, and the theoretical groundwork for understanding the photovoltaic phenomenon was laid only at the beginning of this century. As early as the end of the 19th century, the phenomenon of light shining on a liquid cell producing an electric current was noticed, but no explanation was available. Then just after the start of the 20th century, Albert Einstein offered an explanation for a similar phenomenon, the "photoelectric effect" that brought him the Nobel Prize in physics. This laid the groundwork for an understanding of what we call the "photovoltaic effect".
Further application of the quantum concept led to the development during the 1930's of a whole new way of dealing with matter and energy called Quantum Mechanics. This science was used to develop the new solid state technology that pervades our lives today. Key discoveries made at the Bell Telephone Research Laboratories in the mid-1950's led to the transistor and the first practical solid state solar cell.
A few small modules were made using reject space cells, but this was not a real manufacturing effort. Then the early 1970's saw a worldwide push for alternative renewable sources of energy, and photovoltaics were seen as a real possible solution. Some of the first applications for early photovoltaic modules were, for example, low power warning systems on offshore buoys. However, these early terrestrial models were not mass-produced because they were practically handmade. In the late 1970's, the photovoltaic industry attracted the interest of large energy companies and government agencies. With their investment of capital, a tremendous acceleration in module development took place. Today whole product lines are available with modules designed to withstand environmental wear for decades. As automation, better designs and improved manufacturing techniques have been applied to photovoltaics, the price has dropped significantly. During the space program, prices were as high as $200/watt, whereas today prices have dropped to less than $5/watt. |
||||||
 To observe the photoelectric effect, light was shined on a metal surface, and an electric current could be detected coming off the metal. Einstein explained the observed phenomenon by capitalizing on the recently introduced idea of "quantized" energy levels, and described light itself as being made of a flow of minuscule "photons" or particles of light energy. When photons impinge on a metal, some "knock out" electrons from metal atoms, much like a billiard ball will knock another ball away when the two collide.
To observe the photoelectric effect, light was shined on a metal surface, and an electric current could be detected coming off the metal. Einstein explained the observed phenomenon by capitalizing on the recently introduced idea of "quantized" energy levels, and described light itself as being made of a flow of minuscule "photons" or particles of light energy. When photons impinge on a metal, some "knock out" electrons from metal atoms, much like a billiard ball will knock another ball away when the two collide.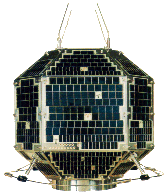 The space race of the late 1950's and 1960's spurred improvements in solar cell design and efficiency. The cells were perfect sources of electric power for satellites because they were rugged, lightweight and could meet the low power requirements reliably. However, the drive to make space qualified solar cells efficient and lightweight led to high costs, making them uneconomical for use on the earth where low price is the main concern.
The space race of the late 1950's and 1960's spurred improvements in solar cell design and efficiency. The cells were perfect sources of electric power for satellites because they were rugged, lightweight and could meet the low power requirements reliably. However, the drive to make space qualified solar cells efficient and lightweight led to high costs, making them uneconomical for use on the earth where low price is the main concern.